The research paper was accepted (Adv. Energ. Sustain. Res.)
Asad Ali, Guo Huang, et al., Selective Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Phenol to Benzoquinone via Water Splitting Using a Nonprecious Metal-Based Electrocatalyst. Adv. Energy Sustainability Res. 2025, 2500108
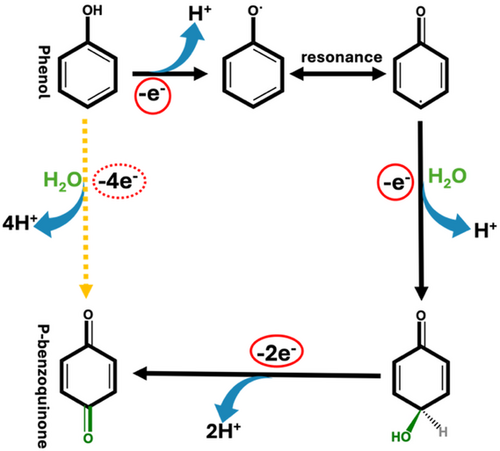
ABSTRACT: Chemicals derived from biomass lignin, with phenolic compounds, are particularly valuable in organic synthesis and catalytic conversion. The electrochemical conversion of biomass materials has gained significant attention in recent years as a sustainable means of producing value-added chemicals. A green process has been developed utilizing electrochemistry to convert inexpensive, readily available phenol derived from lignin into para-benzoquinone, a valuable chemical widely used in the manufacturing and chemical industries. For the first time, a novel electrocatalytic oxidation system is achieved with high 96.2% conversion of phenols to para-benzoquinone with 83.3% selectivity using a nonprecious metal-based electrocatalyst. The high conversion and selectivity are driven by the excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance of carbon felt in the reaction, alongside the redox chemistry of the NiFeB catalyst. This innovative approach not only provides an efficient method for electrochemically producing hydrogen and valuable lignin-derived compounds, but it also lays the foundation for a continuous, sustainable synthesis of para-benzoquinone.
This work supports the EPOCH project by providing a sustainable electrochemical route for converting lignin-derived phenols to para-benzoquinone using a cost-effective, non-precious metal catalyst, advancing green chemical production from biomass.